GEOGRAPHY
Had the asteroid struck a different location, the outcome might have been very different. (BBC)
Zoom in on the Chicxulub impact crater, ground zero for the demise of the dinosaurs.

Illustration by Franco Tempesta, National Geographic
Discussion Ideas
- How did an asteroid, comet, or other space rock lead to the demise of the dinosaurs?
- The impactor didn’t directly cause any extinctions. Instead, it induced a “global winter” (sometimes called an “impact winter”).
- The global winter was created by the injection of tons of sulfur into Earth’s atmosphere. The sulfur was emitted as tons of gypsum (a common sulfate mineral) evaporated upon the asteroid’s impact. As sulfur enters the stratosphere, it forms sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid aerosols cooled Earth’s surface by reflecting solar radiation and inhibiting atmospheric circulation. (This process, called stratospheric aerosol injection, is a candidate for climate engineering to mitigate the current trend of global warming.)
- The global winter led to the demise of about 75% of all life on Earth, including all non-avian dinosaurs. This phenomenon, called the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, began almost immediately. “All these fossils occur in a layer no more than 10 centimeters (4 inches) thick,” says one paleontologist. “They died suddenly and were buried quickly … [T]his is a moment in geological time. That’s days, weeks, maybe months. But this is not thousands of years; it’s not hundreds of thousands of years. This is essentially an instantaneous event.”
- “In this cold, dark world, food ran out of the oceans within a week, and shortly after on land. With nothing to eat anywhere on the planet, the mighty dinosaurs stood little chance of survival.”
- The Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event lasted thousands of years, and ecosystems took about 30 million years to recover.
- The impactor didn’t directly cause any extinctions. Instead, it induced a “global winter” (sometimes called an “impact winter”).
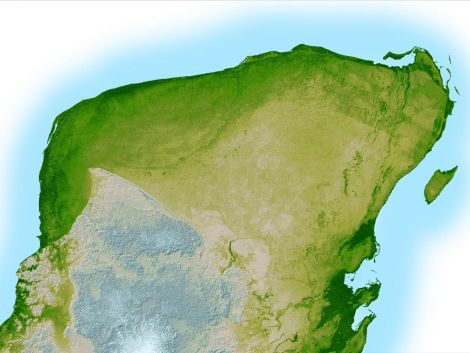
Image courtesy SRTM Team NASA/JPL/NIMA
- Where on Earth did the space rock hit?
- The overwintering asteroid crashed into the Gulf of Mexico, just off the northwest corner of the Yucatan Peninsula in what is today Mexico. The impact crater is known as the Chicxulub crater. The Chicxulub impactor is estimated to have been about 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) wide, and left a crater about 180 kilometers (110 miles) in diameter and 20 kilometers (12 miles) deep.
- The Chicxulub crater is the third-largest impact crater on Earth, behind the Vredefort crater in South Africa and the Sudbury basin in Canada.
- The overwintering asteroid crashed into the Gulf of Mexico, just off the northwest corner of the Yucatan Peninsula in what is today Mexico. The impact crater is known as the Chicxulub crater. The Chicxulub impactor is estimated to have been about 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) wide, and left a crater about 180 kilometers (110 miles) in diameter and 20 kilometers (12 miles) deep.
- What made the Yucatan the “worst possible place” for an impact?
- “This is where we get to the great irony of the story—because in the end it wasn’t the size of the asteroid, the scale of blast, or even its global reach that made dinosaurs extinct—it was where the impact happened,” says one evolutionary biologist.
- The very shallow depth meant “colossal volumes of sulfur (from the mineral gypsum) were injected into the atmosphere, extending the ‘global winter’ period that followed the immediate firestorm.”
- Had the impactor hit the deep ocean, more water and less rock would have vaporized. “The [sulfur debris] cloud would have been less dense and sunlight could still have reached the planet’s surface, meaning what happened next [the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event] might have been avoided.”
- Did anything survive the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event? The shallow seas of Chicxulub may have been the worst place for an impact for the dinosaurs, but was it one of the best places any other animals?
- Yes! In particular, the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event allowed mammals and plants to (slowly) undergo remarkable evolutions and adaptations during the Paleogene. This was a triumph of the little guy, bottom dwellers, and non-picky eaters.
- little guys: Few tetrapods weighing more than about 25 kilograms (55 pounds) seem to have survived. The largest reptiles to survive included crocodilians and turtles. Birds survived, as did all major mammal lineages (if not specific species).
- bottom dwellers: Deep-sea organisms were better able to survive the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, as they rely less on phytoplankton than those in the epipelagic, or sunlight zone.
- non-picky eaters: Terrestrial plant life was radically disrupted, which had the most staggering impact on life (and death) across the planet. Lacking nutrient-rich autotrophs as a food source, strict herbivores went extinct. So did strict carnivores. Omnivores, insectivores, and scavengers were better able to survive the event, likely due to an increase in their food sources.
- Yes! In particular, the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event allowed mammals and plants to (slowly) undergo remarkable evolutions and adaptations during the Paleogene. This was a triumph of the little guy, bottom dwellers, and non-picky eaters.
TEACHERS TOOLKIT
BBC: Dinosaur asteroid hit ‘worst possible place’
Nat Geo: Chicxulub Impact Crater illustration
Nat Geo: What is a crater? reference
Wikipedia: Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (featured article)
Wikipedia: Chicxulub crater (featured article)


Dinosaur is really amazing animal in the world!
The dinosaur give deeply affection, so if someday,if they came back ,how human to live.